In today’s increasingly electrified world, the safe and efficient management of electrical power within homes, commercial buildings, and industrial facilities is non-negotiable.
Often overlooked yet absolutely vital, power distribution boards ensure that electricity is distributed seamlessly and safely across various circuits. In this guide, we’ll break down what they are, how they function, and where they are commonly used.
What is a Power Distribution Board?
. Its main role is to take incoming electrical power from a single source and divide it into multiple circuits, each of which can power different parts of a building or facility. By doing this, it makes the control and protection of electrical supply both manageable and organized.
In simple terms, think of a distribution board as the central hub where electricity is routed and monitored, ensuring that power reaches the right places without overloading any part of the system.
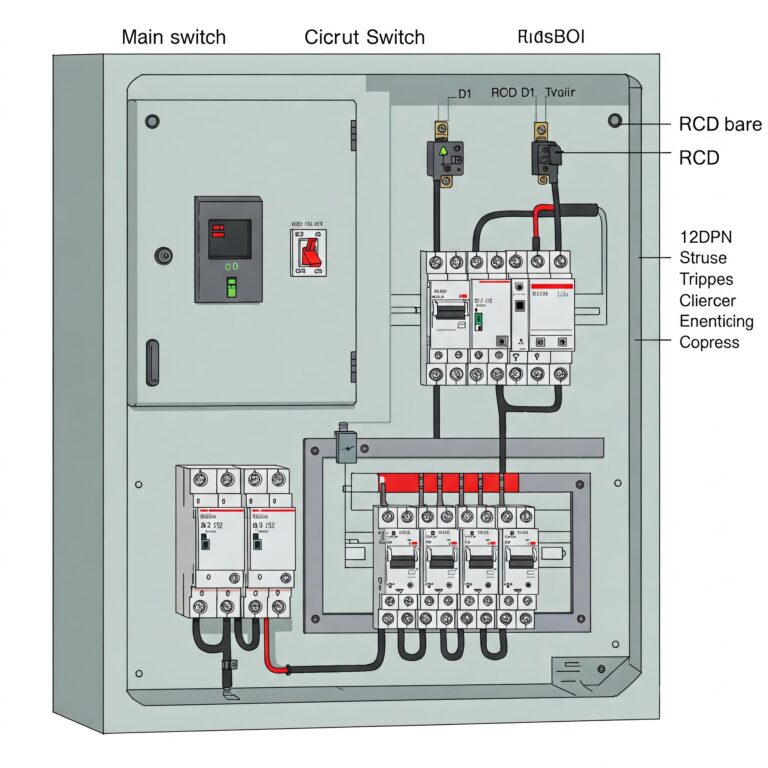
Key Components of a Power Distribution Board
To understand how a PDB functions, it’s important to look at its core components:
-
Main Switch: This regulates the total electrical flow into the distribution board and enables a full shutdown when required.
-
Circuit Breakers: These devices protect individual circuits by cutting off power if there’s an overload or short circuit.
Once the problem is fixed, the circuit breaker can be reset to restore power. -
Busbars: These metal strips or bars conduct electricity within the board, distributing power to various circuits.
-
Residual Current Devices (RCDs): These enhance safety by detecting imbalances in current flow and disconnecting circuits in the event of leakage or faults.
-
Fuses: Although less common today due to circuit breakers, fuses still serve as safety devices that protect circuits by breaking the connection when excess current flows.
How Does a Power Distribution Board Work?
When electrical power enters a building, it first reaches the main switch of the distribution board. From here, the current is distributed through busbars to various circuit breakers. Each breaker channels electricity to a dedicated circuit — for example, lighting, heating, or appliances.
. This action prevents potential damage and reduces the risk of fire hazards.
Benefits of Using a Power Distribution Board

-
Enhanced Safety: Circuit breakers and protective devices minimize the risk of electrical fires and accidents.
-
Efficient Power Management: Distributing power across multiple circuits ensures balanced loads, reducing strain on the system.
-
Flexibility: Modern PDBs can be designed to accommodate future expansions, making it easy to add new circuits as needs evolve.
-
Cost Savings: Efficient distribution and protection reduce energy wastage, contributing to lower electricity bills.
Common Applications of Power Distribution Boards
-
Residential Buildings: They distribute electricity to lighting, outlets, appliances, and HVAC systems within homes.
-
Commercial Facilities: Office buildings, malls, and restaurants rely on PDBs to manage power across lighting, computers, and machinery.
-
Industrial Plants: Factories and warehouses use robust PDBs to handle heavy-duty machinery, conveyor systems, and production lines.
-
Data Centers: Reliable distribution boards ensure uninterrupted power supply to servers and critical IT infrastructure.
-
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals use specialized PDBs to manage power in critical areas like operating rooms and intensive care units.
Conclusion
Power Distribution Boards are the backbone of any structured electrical system, ensuring electricity flows safely and efficiently to where it’s needed most. Whether in homes, offices, or industrial complexes, their role in modern infrastructure is indispensable. Understanding how they function and where they are applied not only highlights their importance but also empowers facility managers, homeowners, and engineers to make informed decisions about electrical safety and efficiency.